Select Question Set:
In the system shown in the figure, the strings and pulleys are ideal, and the block \(A\) moves downward while \(B\) moves to the right. \(A, B \) have equal masses. The acceleration of the block \(B\) is:

1.
\(\dfrac{g}{2}\)
2.
\(\dfrac{g}{5}\)
3.
\(\dfrac{2g}{5}\)
4.
\(g\)
Subtopic: Application of Laws |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
Two smooth balls \(A,B \) of radius \(10\) cm each are placed in a cylinder of diameter \(30\) cm, as shown. The upper ball \((A)\) has a mass of \(2\) kg, while the lower ball \((B)\) has a mass of \(4\) kg. The system is at rest. Let the force exerted on the ball \(A\) by the cylinder be \(F_1\) along the horizontal (as shown) and that on the ball \(B,\) along the horizontal be \(F_2\) (as shown). Then:


| 1. | \(F_1 < F_2\) |
| 2. | \(F_1 = F_2\) |
| 3. | \(F_1 >F_2\) |
| 4. | the relationship between \(F_1\) and \(F_2\) depends on the mass of the cylinder |
Subtopic: Tension & Normal Reaction |
61%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
Two blocks of weight \(1\) kg and \(2\) kg are placed in contact with each other on a smooth horizontal plane. Horizontal forces are applied to the blocks as shown. The blocks move together only if:

1. \(F\leq10\) N
2. \(F>10\) N
3. \(F\leq20\) N
4. \(F>20\) N

1. \(F\leq10\) N
2. \(F>10\) N
3. \(F\leq20\) N
4. \(F>20\) N
Subtopic: Application of Laws |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
A constant force \(F\) is applied to the string so that the \(3\) kg block does not move, but the \(5\) kg block moves horizontally. The acceleration of the \(5\) kg block is: (take \(g=10\) m/s2)


| 1. | \(6\) m/s2 | 2. | \(3\) m/s2 |
| 3. | \(1.5\) m/s2 | 4. | \(1.2\) m/s2 |
Subtopic: Application of Laws |
71%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
The system shown in the diagram is in equilibrium. Assuming that the strings and pulleys are ideal, the ratio of the masses, \(\dfrac{m_1}{m_2}=\)
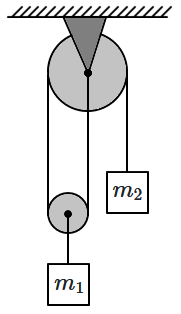

| 1. | \(4\) | 2. | \(2\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) |
a,
Subtopic: Application of Laws |
64%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
Select the correct option based on statements below:
| Assertion (A): | Newton's law of action and reaction is a consequence of Newton's law of inertia. |
| Reason (R): | Newton's law of inertia implies that any body that is not acted upon by external forces cannot change its state of rest or uniform motion. |
| 1. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 2. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
| 3. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
Subtopic: Newton's Laws |
64%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
Assume that at the moment of lift-off, the rate at which gases are ejected is \(r\) (kg/s) and the speed of the exhaust is \(u\) (m/s). If the rocket has a mass \(m\) (with fuel and payload) and its acceleration is zero, but it has lifted off, then,

1. \(mg=ru\)
2. \(mg=ru^2\)
3. \(g=ru\)
4. \(mg=r^2u^2\)

1. \(mg=ru\)
2. \(mg=ru^2\)
3. \(g=ru\)
4. \(mg=r^2u^2\)
Subtopic: Newton's Laws |
77%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
A block of mass \(5\) kg requires a minimum horizontal force of \(20\) N to cause it to move. Take \(g=10\) m/s2. Let \(\mu_s\) be the coefficient of static friction, and \(\mu\small{_ k}\) be that of kinetic friction.

1. \(\mu_s=0.4\)
2. \(\mu_s=\mu{\small_k}=0.4\)
3. \(\mu{\small_ k}=0.4\)
4. \(\mu_s\geq0.4\)

1. \(\mu_s=0.4\)
2. \(\mu_s=\mu{\small_k}=0.4\)
3. \(\mu{\small_ k}=0.4\)
4. \(\mu_s\geq0.4\)
Subtopic: Friction |
53%
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
Given below are two statements:
| Statement I: | Given that the magnitude of the acceleration of a body is constant, the force acting on it must be constant. |
| Statement II: | Newton's second law leads to the statement that the acceleration of a body is directly proportional to the net force acting on it. |
| 1. | Statement I is incorrect and Statement II is correct. |
| 2. | Both Statement I and Statement II are correct. |
| 3. | Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect. |
| 4. | Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect. |
Subtopic: Newton's Laws |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
The system of blocks is pulled up by force as shown in the figure. The force exerted on the \(3\) kg block by the connecting string is:


| 1. | \(80~\text{N}\) | 2. | \(60~\text{N}\) |
| 3. | \(40~\text{N}\) | 4. | \(100~\text{N}\) |
Subtopic: Application of Laws |
70%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
Select Question Set:






