Select Question Set:
The current passing through a certain device doubles when the temperature rises by \(10^{\circ}\text{C}\), in the temperature range from \(0^{\circ}\text{C}\) to \(500^{\circ}\text{C}\). This effect is used to measure the temperature of a sample. The current is measured to be \(5~\text{mA}\) at \(15^{\circ}\text{C}\) and then the next measurement shows a current of \(50~\text{mA}\). The temperature of the new measurement is nearly: (take \(\text{log}_{10}2 \simeq 0.3\), if required)
1. \(150^{\circ}\text{C}\)
2. \(50^{\circ}\text{C}\)
3. \(450^{\circ}\text{C}\)
4. \(25^{\circ}\text{C}\)
Subtopic: Derivation of Ohm's Law |
66%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
All the resistances in circuit are \(2~\Omega\) each, \(E_1=4~\text{V}\) and \(E_2=1~\text{V}\). The potential difference between \(C\) and \(D\) (i.e. \(V_{C}-V_{D}\)) is:


| 1. | \(1.5~\text{V}\) | 2. | \(-1.5~\text{V}\) |
| 3. | \(1.2~\text{V}\) | 4. | \(-1.2~\text{V}\) |
Subtopic: Kirchoff's Voltage Law |
59%
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
A cell is connected between \(A\) and \(B\) and it is observed that \(V_{C}=V_{D}\) while the corresponding ammeter current is also noted. When the cell (between \(A\) and \(B\)) is disconnected, and ends \(B\) and \(C\) are connected: the current through an ammeter \(A\) is found to have the same magnitude (but in opposite direction). Then, the resistance \(R\) is:


| 1. | equals \(400~\Omega.\) |
| 2. | equals \(200~\Omega.\) |
| 3. | can have any value less than \(400~\Omega.\) |
| 4. | cannot be determined from the given information. |
Subtopic: Kirchoff's Voltage Law |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
All the cells, shown in the figure below, are of \(2~\text V,\) and all the resistances are \(1~\Omega.\) When a potential difference \(V\) is applied between \(A\) and \(B,\) the current through the circuit doubles compared to the situation when the potential difference is made zero. Then;
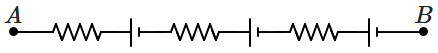
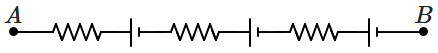
| 1. | \(V=2\) volts, positive at \(A.\) |
| 2. | \(V=2\) volts, negative at \(A.\) |
| 3. | \(V=6\) volts, positive at \(A.\) |
| 4. | \(V=6\) volts, negative at \(A.\) |
Subtopic: Kirchoff's Voltage Law |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
All the resistances in the circuit shown below are \(2~\Omega.\) The equivalent resistance between \(A\) and \(C\) is:


| 1. | \(4~\Omega\) | 2. | \(2~\Omega\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac43~\Omega\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{10}3~\Omega\) |
Subtopic: Combination of Resistors |
73%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
The potential difference \(V_{AB}\) (in volts) is plotted as a function of the resistance \(R.\) The graph is given by:


| 1. |  |
2. | 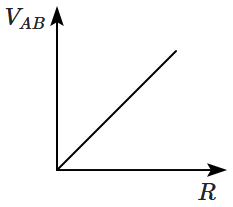 |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Subtopic: Derivation of Ohm's Law |
52%
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
The current flowing through the left \(20~\Omega\) resistor is:


| 1. | \(1~\text A\) | 2. | \(0.5~\text A\) |
| 3. | \(2.5~\text A\) | 4. | \(3~\text A\) |
Subtopic: Kirchoff's Voltage Law |
59%
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
A \(20~\text V\) cell delivers the same power to a \(2~\Omega\) resistor as it does to an \(8~\Omega\) resistor. The internal resistance of the cell is:
1. \(2~\Omega\)
2. \(4~\Omega\)
3. \(6~\Omega\)
4. \(1.6~\Omega\)
1. \(2~\Omega\)
2. \(4~\Omega\)
3. \(6~\Omega\)
4. \(1.6~\Omega\)
Subtopic: Heating Effects of Current |
56%
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
Two cells having emfs \(3\) V and \(2\) V are connected in parallel and they give an emf of \(0.5\) V in the same sense as \(3\) V \(-\) cell. The internal resistances of the cells are \(r_1\) and \(r_2\) respectively. If one cell is reversed, their combined emf becomes \(2.5\) V. The ratio of their internal resistances \(\Big(\dfrac{r_1}{r_2}\Big) \) is:
1. \(1\)
2. \(\dfrac12\)
3. \(\dfrac21\)
4. \(\sqrt2\)
1. \(1\)
2. \(\dfrac12\)
3. \(\dfrac21\)
4. \(\sqrt2\)
Subtopic: Grouping of Cells |
67%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
In the Wheatstone Bridge arrangement shown, the resistance \(P\) is \(2~ \Omega.\) The bridge is initially balanced. If P and Q are interchanged: an amount equal to \(S\) has to be added to \(R\) to restore the balance. The resistance \(Q\) equals (nearly):

1. \(2 ~\Omega\)
2. \(3.2 ~\Omega\)
3. \(4 ~\Omega\)
4. \(6.4 ~\Omega\)

1. \(2 ~\Omega\)
2. \(3.2 ~\Omega\)
3. \(4 ~\Omega\)
4. \(6.4 ~\Omega\)
Subtopic: Wheatstone Bridge |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
Select Question Set:






