Select Chapter Topics:
An equilateral triangular prism of glass \((\mu=1.5)\) is placed in air. A ray of light is incident normally onto the surface \(AB.\) The ray will finally emerge:


| 1. | normally from the surface \(BC.\) |
| 2. | normally from the surface \(AC.\) |
| 3. | either from the surface \(BC\) or \(AC,\) normally. |
| 4. | either from the surface \(BC\) or \(AC,\) at an angle of emergence greater than \(60^{\circ}\) but less than \(90^{\circ}.\) |
Subtopic: Total Internal Reflection |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): | If two converging lenses are introduced into the path of a parallel beam of light, the emerging beam cannot be diverging. |
| Reason (R): | The converging lenses have positive powers. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
Subtopic: Lenses |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
An equi-convex lens of focal length \(20\) cm (in the air) is split into two parts by a surface that has half the curvature of either of its outer surfaces. The ratio of the powers of the two lenses thus formed is:
1. \(3:1\)
2. \(2:1\)
3. \(1:1\)
4. \(-2:1\)
1. \(3:1\)
2. \(2:1\)
3. \(1:1\)
4. \(-2:1\)
Subtopic: Lenses |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
A converging lens is placed near a small object, but the image appears to be extremely large. A second identical lens is placed just behind the first one and very close to it. The final image will be:
| 1. | real and magnified | 2. | real and diminished |
| 3. | real and of the same size | 4. | virtual |
Subtopic: Lenses |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
A ray of light \((1)\) gets reflected partially at the front surface of a thin film of thickness \(t,\) and refractive index \(\mu.\) The reflected ray from the front surface is \(2\) while that emerging due to reflection from the rear surface is \(3.\) Assume that ray \(1\) is incident normally. The optical path difference between rays \(2\) and \(3\) is:


| 1. | \((\mu-1)t\) | 2. | \(2(\mu-1)t\) |
| 3. | \(\mu t\) | 4. | \(2\mu t\) |
Subtopic: Refraction at Plane Surface |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
A thin-walled spherical glass vessel is completely filled with water, and within the water swims a small fish. A person, outside, views this fish when it is motionless – floating at the centre of curvature of the vessel. \(\large\Big( \)\(\mu_{\text{glass}}=1.5,\mu_{\text{water}}=\)\(\dfrac43\Big)\) The image of the fish would appear to be (relative to the viewer):
| 1. | closer than the centre of curvature |
| 2. | farther than the centre of curvature |
| 3. | at the centre of curvature |
| 4. | at infinity |
Subtopic: Refraction at Curved Surface |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
The following diagram shows light travelling from \(A\) to \(B\) after bouncing off a plane mirror at \(P.\) The time taken is \(t_{APB} .\) If, however, light were to take a different path, \(AQB\) (shown by the dotted line), the time taken is \(t_{AQB}.\)
Then,

Then,

| 1. | \(t_{APB}=t_{AQB}\) |
| 2. | \(t_{APB}<t_{AQB}\) |
| 3. | \(t_{APB}>t_{AQB}\) |
| 4. | \(t_{APB}\) may be greater than or less than \(t_{AQB}\) depending on whether \(Q\) is to the left or right of \(P.\) |
Subtopic: Reflection at Plane Surface |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
A thin plane parallel slab (thickness \(t\), refractive index \(\mu\)) is placed just behind a converging lens of focal length \(f.\) If a parallel beam of light is incident on the combination it will converge at a distance of:
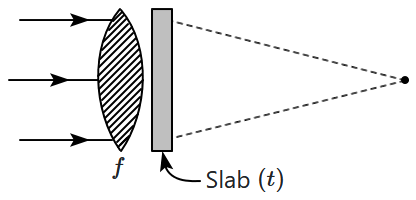

| 1. | \(f\) from the end of the slab. |
| 2. | \(f-\frac{t}{\mu}\) from the end of the slab. |
| 3. | \(f+\frac{t}{\mu}\) from the end of the slab. |
| 4. | \(f+t\Big(1-\frac{1}{\mu}\Big)\) from the end of the slab. |
Subtopic: Refraction at Curved Surface |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): | Parallel rays of light of different colours fail to converge to a point after reflection from a spherical mirror. |
| Reason (R): | The refractive index of any material depends on the frequency of light. |
| 1. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 2. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
| 3. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
Subtopic: Reflection at Spherical Surface |
Level 4: Below 35%
Hints
If a slab of glass (refractive index \(=1.5 \)) were placed on the printed page of a book, the words would appear to be:
| 1. | larger in size by a factor of \(1.5\) |
| 2. | \(1.5\) times smaller in size |
| 3. | of the same size |
| 4. | inverted, and of the same size |
Subtopic: Refraction at Plane Surface |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints






