Select Question Set:
Identify the correct match for A, B, C and D in the given figure:

A
B
C
D
1.
46
46
23
Second
2.
46
23
23
Secondary
3.
46
23
23
Second
4.
23
23
46
Secondary
Subtopic: Seminiferous Tubules & Spermatogenesis | oogenesis |
71%
Level 2: 60%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Match each item in Column-I with one in Column-II and select the correct match from the codes given:
Codes:
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| A. | Insemination | P. | embryonic development |
| B. | Implantation | Q. | transfer of sperms into the female genital tract |
| C. | Gestation | R. | delivery of the baby |
| D. | Parturition | S. | attachment of blastocyst to the uterine wall |
| A | B | C | D | |
| 1. | Q | S | R | P |
| 2. | S | Q | R | P |
| 3. | Q | S | P | R |
| 4. | S | Q | P | R |
Subtopic: Implantation : Part 1 | Implantation : Part 2 |
92%
Level 1: 80%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
There are remarkable differences between the reproductive events in the male and in the female, including:
1. Only I is correct
2. Only II is correct
3. Both I and II are correct
4. Both I and II are incorrect
| I: | sperm formation continues even in old men, but formation of ovum ceases in women around the age of fifty years. |
| II: | sperm formation begins in foetal life and egg formation begins after the onset of puberty. |
1. Only I is correct
2. Only II is correct
3. Both I and II are correct
4. Both I and II are incorrect
Subtopic: Introduction |
91%
Level 1: 80%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
In the given figure, identify the hormones represented by A, B, C and D?


| A | B | C | D | |
| 1. | FSH | LH | Progesterone | Oestrogen |
| 2. | FSH | LH | Oestrogen | Progesterone |
| 3. | LH | FSH | Progesterone | Oestrogen |
| 4. | LH | FSH | Oestrogen | Progesterone |
Subtopic: Menstrual Cycle: Pre Ovulatory Phase | Menstrual Cycle: Luteal Phase |
80%
Level 1: 80%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Identify the correct statements:
1. Only I and II
2. Only I and III
3. Only II and III
4. I, II and III
| I: | The reproductive cycle in the non-primate female mammals is called menstrual cycle. |
| II: | The first menstruation begins at puberty and is called menarche. |
| III: | In human females, menstruation is repeated at an average interval of about 28/29 days, and the cycle of events starting from one menstruation till the next one is called the menstrual cycle. |
1. Only I and II
2. Only I and III
3. Only II and III
4. I, II and III
Subtopic: Menstrual Cycle: Pre Ovulatory Phase | Menstrual Cycle: Luteal Phase |
83%
Level 1: 80%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
For maintenance of the endometrium, the corpus luteum secretes large amounts of:
| 1. | Progesterone | 2. | Oestrogen |
| 3. | LH | 4. | FSH |
Subtopic: Female Reproductive System-1 | Female Reproductive System-2 |
93%
Level 1: 80%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Consider the given two statements:
| Assertion (A): | Not all copulations lead to fertilisation and pregnancy. |
| Reason (R): | Fertilisation can only occur if the ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to the ampullary region of the oviduct. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) explains (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) does not explain (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
Subtopic: Female Reproductive System-1 | Female Reproductive System-2 |
95%
Level 1: 80%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
What induces the completion of the meiotic division of the secondary oocyte?
1. LH surge
2. Ovulation itself
3. Contact of sperm with zona pellucida
4. Entry of sperm into the cytoplasm of oocyte
1. LH surge
2. Ovulation itself
3. Contact of sperm with zona pellucida
4. Entry of sperm into the cytoplasm of oocyte
Subtopic: Female Reproductive System-1 | Female Reproductive System-2 | Female External Genitalia |
60%
Level 2: 60%+
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Human chorionic gonadotropin is secreted by trophoblast cells as well and this hormone resembles in action to:
| 1. | LH | 2. | FSH |
| 3. | Oestrogen | 4. | Progesterone |
Subtopic: Implantation |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Which alphabet in the given figure represents the structure that carries two pairs of centrioles?
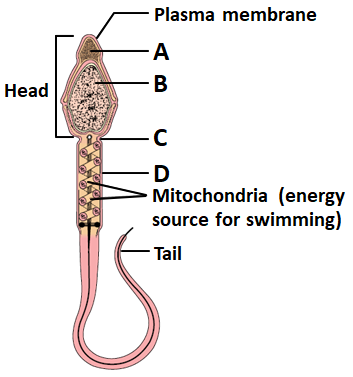
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D

1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
Subtopic: Male Reproductive Duct System | Semen and Male Fertility |
57%
Level 3: 35%-60%
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Select Question Set:






