Consider the circuit shown in the figure given below. The input voltage is \(V_i\), the current through the diode is \(I_z\), and the current through the load is \(I_L\).

1.
\(\text{If} ~{V_i}= 15~\text{V}~\text{and}~{R_L}= 40~\Omega, ~\text{and}~{I_z}= 0.375~\text{A}\)
2.
\(\text{If} ~{V_i}= 10~\text{V}~\text{and}~{R_L}= 5~\Omega, ~\text{and}~{I_L}=1~\text{A}\)
3.
\(\text{If} ~{V_i}= 20~\text{V}~\text{and}~{R_L}= 20~\Omega, ~\text{and}~{I_z}= 0.25~\text{A}\)
4.
\(\text{If} ~{V_i}= 20~\text{V}~\text{and}~{R_L}= 10~\Omega, ~\text{and}~{I_z}= 0.5~\text{A}\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

Consider the following two statements and mark the correct option.
| (I) | \(\text{If}~V_i>2~\text{V}, ~\text{then}~V_o = V_i\) |
| (II) | \(\text{If}~V_i<2~\text{V}, ~\text{then}~V_o = 2~\text{V}\) |
| 1. | (I) is True. |
| 2. | (II) is True. |
| 3. | (I) and (II) are both True. |
| 4. | (I) and (II) are both False. |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| Assertion (A): | The resistance of a photodiode decreases when light having photons of sufficient energy is incident on it. |
| Reason (R): | When energetic photons fall on the \(\mathrm{p\text{-}n}\) junction of a photodiode, electron-hole pairs are created due to the breaking of the valence bonds. |
| 1. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 2. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
| 3. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | \(\dfrac{30}{\sqrt2}~\text{V}\) | 2. | \(15 ~\text{V}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{15}{\sqrt2}~\text{V}\) | 4. | \(10 ~\text{V}\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

The current through the circuit is:
1. \(40\) mA
2. \(54\) mA
3. \(33\) mA
4. \(26\) mA

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

1. \(\text{If}~V_{AB}>0, V_{AX}>0\)
2. \(\text{If}~V_{AB}>0, V_{XY}>0\)
3. \(\text{If}~V_{AB}<0, V_{XY}>0\)
4. \(\text{If}~V_{AB}<0, V_{AX}>0\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| \(A\) | \(B\) | \(C\) | \(Y\) (Output) |
| \(1\) | \(X\) | \(1\) | \(1\) |
| \(0\) | \(1\) | \(X\) | \(1\) |
| All other cases | \(0\) | ||
| 1. |  |
| 2. |  |
| 3. |  |
| 4. |  |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
Here, \(T=\) absolute temperature, \(V=\) voltage across the diode, \(k=\) Boltzmann's constant and \(i_0=\) the drift current.
Then, the differential resistance of the diode \(\left(\dfrac{dV}{di}\right)\) is given by:
1. \(\text{(constant)}i\)
2. \(\text{(constant)}i^2\)
3. \(\dfrac{\text{constant}}{i}\)
4. \(\text{(constant)}e^{-\beta i},~\beta\text{-constant}\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. |  |
| 2. | 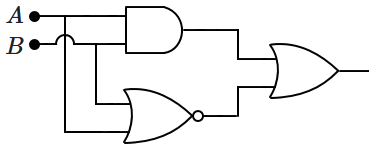 |
| 3. |  |
| 4. |  |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

This diode is connected with a resistance of \(5~\Omega\) in series with it as shown below:

Which of the following shows the dependence of the voltage \(V_{AB}\) and the current \(i,\) when the diode is forward-biased?
(\(V_{AB}\) in volt, \(i\) in ampere)
| 1. | \(V_{A B}=i\cdot5+0.6\) |
| 2. | \(V_{A B}=i\cdot5-0.6\) |
| 3. | \(V_{A B}=i\cdot5+(0.6-5)\) |
| 4. | \(V_{A B}=i\cdot5+\left(0.6+5\right)\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.






