The peak voltage in the output of a half-wave rectifier is \(30 ~\text{V}.\) The RMS voltage of the output wave is: (assuming no distortion in wave)
1.
\(\dfrac{30}{\sqrt2}~\text{V}\)
2.
\(15 ~\text{V}\)
3.
\(\dfrac{15}{\sqrt2}~\text{V}\)
4.
\(10 ~\text{V}\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

The current through the circuit is:
1. \(40\) mA
2. \(54\) mA
3. \(33\) mA
4. \(26\) mA

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

1. \(\text{If}~V_{AB}>0, V_{AX}>0\)
2. \(\text{If}~V_{AB}>0, V_{XY}>0\)
3. \(\text{If}~V_{AB}<0, V_{XY}>0\)
4. \(\text{If}~V_{AB}<0, V_{AX}>0\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| \(A\) | \(B\) | \(C\) | \(Y\) (Output) |
| \(1\) | \(X\) | \(1\) | \(1\) |
| \(0\) | \(1\) | \(X\) | \(1\) |
| All other cases | \(0\) | ||
| 1. |  |
| 2. |  |
| 3. |  |
| 4. |  |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
Here, \(T=\) absolute temperature, \(V=\) voltage across the diode, \(k=\) Boltzmann's constant and \(i_0=\) the drift current.
Then, the differential resistance of the diode \(\left(\dfrac{dV}{di}\right)\) is given by:
1. \(\text{(constant)}i\)
2. \(\text{(constant)}i^2\)
3. \(\dfrac{\text{constant}}{i}\)
4. \(\text{(constant)}e^{-\beta i},~\beta\text{-constant}\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. |  |
| 2. | 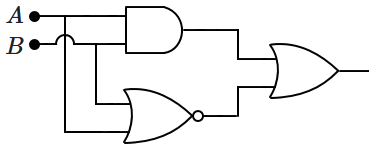 |
| 3. |  |
| 4. |  |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

This diode is connected with a resistance of \(5~\Omega\) in series with it as shown below:

Which of the following shows the dependence of the voltage \(V_{AB}\) and the current \(i,\) when the diode is forward-biased?
(\(V_{AB}\) in volt, \(i\) in ampere)
| 1. | \(V_{A B}=i\cdot5+0.6\) |
| 2. | \(V_{A B}=i\cdot5-0.6\) |
| 3. | \(V_{A B}=i\cdot5+(0.6-5)\) |
| 4. | \(V_{A B}=i\cdot5+\left(0.6+5\right)\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
(consider the diodes as ideal.)

| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | \(V_o=V_i+E\) |
| 2. | \(V_o=V_i-E\) |
| 3. | \(V_o=V_i,\) only when \(V_i>E\) |
| 4. | \(V_o=V_i,\) only when \(V_i<E\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

1. \(V_A>V_B+V_0\)
2. \(V_A<V_B+V_0\)
3. \(V_A>V_B-V_0\)
4. \(V_A<V_B-V_0\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.






