An Atwood's machine with blocks of masses \(3\) kg and \(2\) kg is set up in a laboratory. The string is taut and the blocks start moving at \(t=0.\)

The relative acceleration of the blocks has the magnitude:
1. \(\dfrac{g}{5}\)
2. \(\dfrac{2g}{5}\)
3. \(\dfrac{3g}{5}\)
4. \(\dfrac{4g}{5}\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

The work done by tension on the \(3\) kg block has a magnitude \(W_1\) while the work done by gravity on the same block has a magnitude \(W_2,\) since the beginning of motion.
| 1. | \(W_1=W_2\) |
| 2. | \(W_1>W_2\) |
| 3. | \(W_1<W_2\) |
| 4. | Any of the above can be true |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
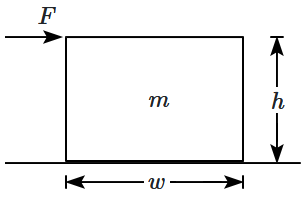
| 1. | \(N\) increases as \(F\) increases. |
| 2. | \(N\) does not act through the center of the block. |
| 3. | \(f\) is greater than \(F.\) |
| 4. | \(f\) acts through the centre of the block. |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | \(m\dfrac{g+2a}{g+a}\) |
| 2. | \(m\dfrac{g+a}{g}\) |
| 3. | \(m\dfrac{g+a}{a}\) |
| 4. | \(m\dfrac{g+2a}{g}\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

1. \(F\)
2. \(2F\)
3. \(\sqrt2F\)
4. \(\dfrac{F}{\sqrt2}\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

1. \(g\)
2. \(\dfrac{g}{2}\)
3. \(\dfrac{g}{\sqrt2}\)
4. \(g\sqrt2\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

1. \(8\) N
2. \(6\) N
3. \(4\) N
4. \(2\) N

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

1. \(10\) N
2. \(10 \sqrt 2\) N
3. \(5 \sqrt 2\) N
4. \(5\) N

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | \(\dfrac{g}{2}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{g}{5}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{2g}{5}\) | 4. | \(g\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | \(F_1 < F_2\) |
| 2. | \(F_1 = F_2\) |
| 3. | \(F_1 >F_2\) |
| 4. | the relationship between \(F_1\) and \(F_2\) depends on the mass of the cylinder |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.






