An equiconvex lens of focal length \(50\) cm is made of glass of refractive index, \(\mu=1.5.\) It is split into two identical plano-convex lenses, and a glass-slab of the same refractive index, and of thickness \(300\) cm is inserted between the two half-lenses (plano-convex). When a parallel beam is incident on the combination, the emerging beam:
1.
focuses at a distance of \(100\) cm from the second lens.
2.
focuses at \(200\) cm from second lens.
3.
focuses at \(150\) cm from second lens.
4.
emerges as a parallel beam.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | converging mirror of focal length \(200\) cm. |
| 2. | converging mirror of focal length \(100\) cm. |
| 3. | diverging mirror of focal length \(200\) cm. |
| 4. | diverging mirror of focal length \(100\) cm. |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | \(90^{\circ}\) | 2. | \(45^{\circ}\) |
| 3. | \(60^{\circ}\) | 4. | \(30^{\circ}\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
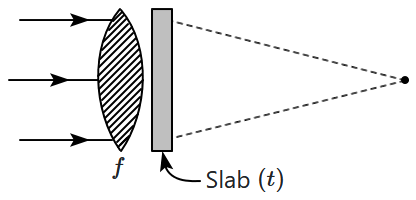
| 1. | \(f\) from the end of the slab. |
| 2. | \(f-\frac{t}{\mu}\) from the end of the slab. |
| 3. | \(f+\frac{t}{\mu}\) from the end of the slab. |
| 4. | \(f+t\Big(1-\frac{1}{\mu}\Big)\) from the end of the slab. |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
1. \(60\) cm
2. \((60+30\sqrt2)\) cm
3. \(60\sqrt2\) cm
4. \(30\sqrt2\) cm

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | \(30\) cm | 2. | \(60\) cm |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{20}3\) cm | 4. | \(\dfrac{40}{3}\) cm |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | \(\dfrac32\) | 2. | \(2\) |
| 3. | \(\sqrt{\dfrac32} \) | 4. | \(\sqrt2\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

1. \(\hat i-2\hat j-\hat k\)
2. \(\hat i+\hat k-2\hat j\)
3. \(-\hat i+2\hat j+\hat k\)
4. \(\hat i+2\hat j+\hat k\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | normally from the surface \(BC.\) |
| 2. | normally from the surface \(AC.\) |
| 3. | either from the surface \(BC\) or \(AC,\) normally. |
| 4. | either from the surface \(BC\) or \(AC,\) at an angle of emergence greater than \(60^{\circ}\) but less than \(90^{\circ}.\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| Assertion (A): | If two converging lenses are introduced into the path of a parallel beam of light, the emerging beam cannot be diverging. |
| Reason (R): | The converging lenses have positive powers. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.






