A solenoid has a core of material with relative permeability \(400.\) The windings of the solenoid are insulated from the core and carry a current of \(2~\text{A}\). If the number of turns is \(1000\) per metre, the magnetising field \(B\) is:
1.
\(10~\text{T}\)
2.
\(1~\text{T}\)
3.
\(0.1~\text{T}\)
4.
\(2~\text{T}\)
A solenoid has a core of material with relative permeability \(400\). The windings of the solenoid are insulated from the core and carry a current of \(2~\text{A}\). If the number of turns is \(1000\) per metre, the magnetization, \(M\) is:
| 1. | \(8\times10^{5}~\text{A/m}\) | 2. | \(6\times10^{5}~\text{A/m}\) |
| 3. | \(6.5\times10^{5}~\text{A/m}\) | 4. | \(8.9\times10^{5}~\text{A/m}\) |
A domain in ferromagnetic iron is in the form of a cube of side length \(1~\mu\text m.\) The maximum possible dipole moment is:
[The molecular mass of iron is \(55~\text{g/mole}\) and its density is \(7.9~\text{g/cm}^3.\) Assume that each iron atom has a dipole moment of \(9.27\times 10^{-24}~\text{Am}^2\)]
1. \(8.0\times10^{-13}~\text{Am}^2\)
2. \(8.0\times10^{-12}~\text{Am}^2\)
3. \(7.0\times10^{-13}~\text{Am}^2\)
4. \(7.0\times10^{-12}~\text{Am}^2\)
Figure shows the graph for magnetic hysteresis for a ferromagnetic materail. From the graph, magnetic retentivity for the material is-
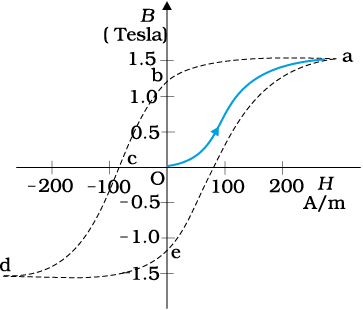
1. 2.5 T
2. 1.2 T
3. 1 T
4. 4 T
A solenoid has a core of material with relative permeability \(400.\) The windings of the solenoid are insulated from the core and carry a current of \(2~\text A.\) If the number of turns is \(1000\) per metre, the magnetic field intensity \(H\) is:
1. \(2\times10^2~\text{A/m}\)
2. \(2\times10^3~\text{A/m}\)
3. \(2~\text{A/m}\)
4. \(20~\text{A/m}\)
In the magnetic meridian of a certain place, the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field is \(0.26~\text{G}\) and the dip angle is \(60^{\circ}\). The magnetic field of the earth at this location is:
1. \(0.25~\text{G}\)
2. \(0.20~\text{G}\)
3. \(0.35~\text{G}\)
4. \(0.52~\text{G}\)
The earth’s magnetic field at the equator is approximately 0.4 G. The earth’s dipole moment is:
(Radius of earth, \(R_{E}=6.4\times10^{6} \) m)
1. \(1.05\times10^{23}\) A-m2
2. \(8.0\times10^{22}\) A-m2
3. \(4.5\times10^{23}\) A-m2
4. \(2.10\times10^{23}\) A-m2
Which one of the following is correct?
| 1. | The magnetic field lines also represent the lines of force on a moving charged particle at every point. |
| 2. | The magnetic field lines can be entirely confined within the core of a toroid, but not within a straight solenoid. |
| 3. | A bar magnet exerts a torque on itself due to its own field. |
| 4. | The magnetic field arises due to stationary charges. |
Which of the following is the correct representation of magnetic field lines?

| 1. | (g), (c) | 2. | (d), (f) |
| 3. | (a), (b) | 4. | (c), (e) |
The figure shows a small magnetized needle \(P\) placed at a point \(O.\) The arrow shows the direction of its magnetic moment. The other arrows show different positions (and orientations of the magnetic moment) of another identical magnetized needle \(Q.\) Then:

| 1. | In \(P Q_1\) and \(P Q_2\) configuration, the system is not in equilibrium. |
| 2. | In \(P Q_3 \) and \(P Q_6\) configuration, the system is unstable. |
| 3. | In \(P Q_5\) and \(P Q_4\) configuration, the system is stable. |
| 4. | \(P Q_5\) configuration corresponds to the lowest potential energy among all the configurations shown. |






