| Assertion (A): | The impedance of a capacitance increases as the frequency increases. |
| Reason (R): | The charge and voltage across a capacitance are directly proportional to each other. |
Choose the correct option from the given ones:
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | the current is always zero |
| 2. | the current has identical positive and negative fluctuations |
| 3. | the current is positive for exactly half the time and negative for the remaining time |
| 4. | the current may be positive, negative or zero (during the interval) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
1. \(30^{\circ}\)
2. \(60^{\circ}\)
3. \(45^{\circ}\)
4. \(90^{\circ}\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | glow brighter |
| 2. | glow dimmer |
| 3. | glow the same |
| 4. | first glow brighter, then dims gradually |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | equal to \(300~\text V\) |
| 2. | less than \(300~\text V\) |
| 3. | greater than \(300~\text V\) |
| 4. | zero |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | \(f_o = \dfrac{10^3 + 10^5}{2}\) Hz |
| 2. | \(f_o > \dfrac{10^3 + 10^5}{2}\) Hz |
| 3. | \(f_o < \dfrac{10^3 + 10^5}{2}\) Hz |
| 4. | \(f_o = {10^3 + 10^5}\) Hz |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | \(\dfrac{V_r}{3}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{2V_r}{3}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{V_r}{2}\) | 4. | \(V_r\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | \(2\text{ A}\) | 2. | \(2\sqrt2\text{ A}\) |
| 3. | \(\sqrt2\text{ A}\) | 4. | zero |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
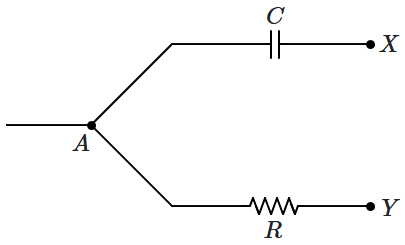
| 1. | zero | 2. | \(\sqrt 2 V_r \) |
| 3. | \(2 V_r\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{V_r}{\sqrt 2}\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. | depends on the ratio \(\dfrac{\omega L}{R}\) |
| 2. | depends on the quantity \(\sqrt{(\omega L)^2+R^2}\) |
| 3. | depends on \(L\) and \(R,\) but not on \(\omega\) |
| 4. | is independent of \(L,R,\omega\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.






