
1. \(120~\text{Hz}\)
2. \(240~\text{Hz}\)
3. \(360~\text{Hz}\)
4. \(180~\text{Hz}\)

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | \(\dfrac{ 1}{2L} \sqrt {\dfrac{T}{m}}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{1}{4 L} \sqrt{\dfrac{T}{m}}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{1}{2} \sqrt{\dfrac{TL}{2m}}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{1}{2} \sqrt{\dfrac{T}{m L}}\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | increases | 2. | decreases |
| 3. | first increases and then decreases | 4. | remains constant |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | \(u+\dfrac{u}{100}\) | 2. | \(u-\dfrac{u}{100}\) |
| 3. | \(u+\dfrac{u}{200}\) | 4. | \(u-\dfrac{u}{200}\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.
| 1. | \(L_A=2L_B\) | 2. | \(L_A=\Large{\frac{L_B}{2}}\) |
| 3. | \(2L_A=3L_B\) | 4. | \(\Large{\frac{L_A}{2}=\frac{L_B}{3}}\) |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

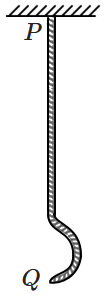
The speed of the pulse is:
| 1. | maximum at \(A,\) minimum at \(O\) |
| 2. | minimum at \(A,\) maximum at \(O\) |
| 3. | uniform |
| 4. | minimum at \(A\) and \(O,\) maximum in the middle |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

| 1. |  |
| 2. |  |
| 3. |  |
| 4. |  |

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.

To unlock all the explanations of this course, you need to be enrolled.




