A pipe, \(30.0\) cm long, is open at both ends.
(i)
Which harmonic mode of the pipe resonates a \(1.1\) kHz source?
(ii)
Will resonance with the same source be observed if one end of the pipe is closed?
Take the speed of sound in air as \(330\) m s–1.
(i)
(ii)
1.
First
No
2.
Second
No
3.
First
Yes
4.
Second
Yes
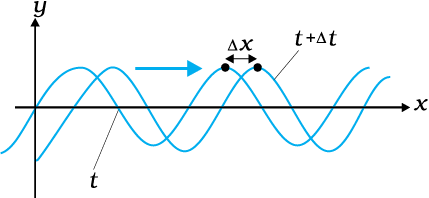
The given diagram shows the progression of a harmonic wave from time t to t + where the crest of the wave displaces by . Then the speed of the wave will be:
A rocket is moving at a speed of \(200\) ms–1 towards a stationary target. While moving, it emits a wave of frequency \(1000\) Hz. Some of the sound reaching the target gets reflected back to the rocket as an echo. The frequency of the sound as detected by the target and the frequency of the echo as detected by the rocket respectively are: (speed of sound = \(330\) m/s)
1. \(4080\) Hz and \(2540\) Hz
2. \(1000\) Hz and \(1000\) Hz
3. \(2540\) Hz and \(4080\) Hz
4. \(2540\) Hz and \(2540\) Hz
Two sitar strings A and B playing the note ‘Dha’ are slightly out of tune and produce beats of frequency \(5\) Hz. The tension of the string B is slightly increased and the beat frequency is found to decrease to \(3\) Hz. What is the original frequency of B if the frequency of A is \(427\) Hz?
1. \(432\) Hz
2. \(424\) Hz
3. \(430\) Hz
4. \(422\) Hz
The speed of sound in air at standard temperature and pressure is:
(Given the mass of \(1\) mole of air is \(29.0\times10^{-3}~\text{kg}\) and \(\gamma=7/5 \text)\)
1. \(240 ~\text{m/s}\)
2. \(331.5~\text{m/s}\)
3. \(384.5~\text{m/s}\)
4. \(280~\text{m/s}\)
A steel wire \(0.72~\text{m}\) long has a mass of \(5\times10^{-3}~\text{kg}\). If the wire is under tension of \(60~\text{N}\), the speed of transverse waves on the wire will be:
1. \(85~\text{m/s}\)
2. \(83~\text{m/s}\)
3. \(93~\text{m/s}\)
4. \(100~\text{m/s}\)
A wave travelling along a string is described by, \(y(x,~t)=0.005 ~\sin(80.0x-3.0t),\) in which the numerical constants are in SI units. The displacement \(y\) of the wave at a distance \(x = 30.0~\text {cm}\) and time \(t=20~\text{s}\) is:
1. \(0.5~\text{mm}\)
2. \(5~\text{mm}\)
3. \(5~\text{m}\)
4. \(5~\text{cm}\)
A wave travelling along a string is described by, \(y(x,t)=0.005 \text{ sin}(80.0x-3.0t),\) in which the numerical constants are in SI units. The wavelength and the period of the wave respectively are:
1. \(7.85 ~\text{cm}\) and \(2.09 ~\text{s}\)
2. \(7.85 ~\text{cm}\) and \(1.09 ~\text{s}\)
3. \(7.85 ~\text{cm}\) and \(0.09 ~\text{s}\)
4. none of these
The length of the string of a musical instrument is \(90\) cm and has a fundamental frequency of \(120\) Hz. Where should it be pressed to produce a fundamental frequency of \(180\) Hz?
| 1. | \(75\) cm | 2. | \(60\) cm |
| 3. | \(45\) cm | 4. | \(80\) cm |
The following statements are given for a stationary wave:
a. Every particle has a fixed amplitude which is different from the amplitude of its nearest particle.
b. All the particles cross their mean position at the same time.
c. All the particles are oscillating with the same amplitude.
d. There is no net transfer of energy across any plane.
e. There are some particles that are always at rest.
Choose the correct alternatives:
1. (a, b, d, e)
2. (a, c, d, e)
3. (b, c, d)
4. (c, d, e)






