A rod of mass m length l is moving between perpendicular smooth walls as shown. When the rod is at an angle \(\theta\) with horizontal its end \(A\) is moving right with speed \(v\). The speed of end \(B\) is:

1. \(v\cot \theta\)
2. \(v\tan \theta\)
3. \(v\cos \theta\)
4. \(v\sin \theta\)

1. \(v\cot \theta\)
2. \(v\tan \theta\)
3. \(v\cos \theta\)
4. \(v\sin \theta\)
The figure shows a rod of length \(5\) m. Its ends, \(A\) and \(B\), are restrained to moving in horizontal and vertical guides. When the end \(A\) is \(3\) m above \(O\), it moves at \(4\) m/s. The velocity of end \(B\) at that instant is:

1. \(2\) m/s
2. \(3\) m/s
3. \(4\) m/s
4. \(0.20\) m/s
A rod supported on the wall starts slipping down. If the speed of upper-end A is 5 m/s, then the speed with which end B will move to the left, as shown in the figure, is

1. 5 m/s
2. 10 m/s
3. m/s
4. m/s
If the block is being pulled by the rope moving at speed \(v\) as shown, then the horizontal velocity of the block is:

1. \(v\)
2. \(v\cos\theta\)
3. \(\frac{v}{\cos\theta}\)
4. \(\frac{v}{\sin\theta}\)
In the given figure, the spring balance is massless, so the reading of the spring balance will be:

| 1. | \(2\) kg | 2. | \(3.5\) kg |
| 3. | \(2.9\) kg | 4. | \(3.1\) kg |
The strings and pulleys shown in the figure are massless. The reading shown by the light spring balance \(S\) is:

| 1. | \(2.4\) kg | 2. | \(5\) kg |
| 3. | \(2.5\) kg | 4. | \(3\) kg |
In the figure shown the horizontal surface is smooth and the strings are inextensible and the massless pulleys are light. If the acceleration of block \(1\) kg is a, then acceleration of \(3\) kg is:
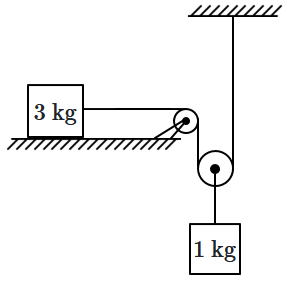
| 1. | \(0\) | 2. | \(2a \) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{a}{2}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{a}{4}\) |
What is the velocity of the block when the angle between the string and the horizontal is \(30^\circ\) as shown in the diagram?

1. \(v_B=v_P\)
2. \(v_B=\frac{v_P}{\sqrt{3}}\)
3. \(v_B=2v_P\)
4. \(v_B=\frac{2v_P}{\sqrt{3}}\)
A ball of mass 1 kg projected with velocity 20 m/s from the origin of an XY coordinate axes at an angle 30° with horizontal. The change in momentum in 1 s is:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Assertion: A safe turn by a cyclist should neither be too fast nor too sharp.
Reason: This is so because it increases the chances of skidding.
1. both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
2. both Assertion and Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
3. Assertion is a true statement but Reason is false.
4. both Assertion and Reason are false statements.






