
1. \(0.4~\text{A}\) and \(0.2~\text{A}\)
2. \(0.2~\text{A}\) and \(0.4~\text{A}\)
3. \(0.1~\text{A}\) and \(0.2~\text{A}\)
4. \(0.2~\text{A}\) and \(0.1~\text{A}\)

1. \({\frac{\left(V_i-V_L\right)}{(n+1) I_L}}\)
2. \({\frac{\left(V_i+V_L\right)}{(n+1) I_L}}\)
3. \({\frac{\left(V_i-V_L\right)}{n I_L}}\)
4. \({\frac{\left(V_i+V_L\right)}{n I_L}}\)
Match the semiconductor devices with their corresponding characteristic graphs labeled \(\mathrm{(a),(b),(c)}\) and \(\mathrm{(d)}.\)

Select the correct sequence from the options given below:
| 1. | \(\mathrm{(a)}-\)Simple diode; \(\mathrm{(b)}-\)Zener diode; \(\mathrm{(c)}-\)Solar cell; \(\mathrm{(d)}-\)Light-dependent resistance |
| 2. | \(\mathrm{(a)}-\)Solar cell; \(\mathrm{(b)}-\)Zener diode; \(\mathrm{(c)}-\)Simple diode; \(\mathrm{(d)}-\)Light-dependent resistance |
| 3. | \(\mathrm{(a)}-\)Zener diode; \(\mathrm{(b)}-\)Simple diode; \(\mathrm{(c)}-\)Solar cell; \(\mathrm{(d)}-\)Light-dependent resistance |
| 4. | \(\mathrm{(a)}-\)Solar cell; \(\mathrm{(b)}-\)Simple diode; \(\mathrm{(c)}-\)Light-dependent resistance; \(\mathrm{(d)}-\)Zener diode |
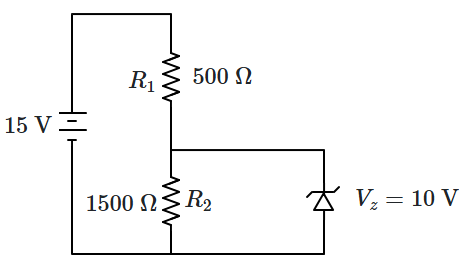
1. \(3.3~\text{mA}\)
2. \(2.5~\text{mA}\)
3. \(5.5~\text{mA}\)
4. \(6.7~\text{mA}\)
The reverse breakdown voltage of a Zener diode is \(5.6~\text{V}\) in the given circuit.
The current \(I_Z\) through the Zener is:
1. \(7~\text{mA}\)
2. \(10~\text{mA}\)
3. \(17~\text{mA}\)
4. \(15~\text{mA}\)
The figure shows a voltage regulator circuit using a Zener diode. The breakdown voltage of the Zener diode is \(6~\text{V},\) and the load resistance is \(R_L=4 ~\text{k}\Omega.\) The series resistance in the circuit is \(R_i=1 ~\text{k} \Omega.\) If the battery voltage \(V_B\) varies from \(8~\text{V}\) to \(16~\text{V},\) what are the minimum and maximum values of the current through the Zener diode?
| 1. | \(0.5~\text{mA}; ~8.5~\text{mA}\) | 2. | \(1.5~\text{mA}; ~8.5~\text{mA}\) |
| 3. | \(1~\text{mA}; ~8.5~\text{mA}\) | 4. | \(0.5~\text{mA}; ~6~\text{mA}\) |
(assume that the \(\mathrm{Ge}\) diode has a large breakdown voltage)
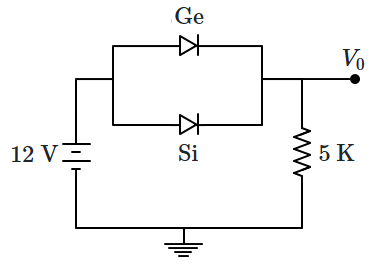
1. \(0.8~\text{V}\)
2. \(0.6~\text{V}\)
3. \(0.2~\text{V}\)
4. \(0.4~\text{V}\)
If a semiconductor photodiode can detect a photon with a maximum wavelength of \(400~\text{nm},\) then the energy of its band gap is:
(take Planck’s constant \(h=6.63 \times 10^{-34} \text { J-s }\) and speed of light \(c=3 \times 10^8\) m/s)
1. \(3.1~\text{eV}\)
2. \(1.1~\text{eV}\)
3. \(2.0~\text{eV}\)
4. \(1.5~\text{eV}\)
With increasing biasing voltage of a photodiode, the photocurrent magnitude:
| 1. | increases initially and saturates finally. |
| 2. | increases initially and after attaining certain value, it decreases. |
| 3. | increases linearly. |
| 4. | remains constant. |











