The electron concentration in an \(\mathrm{n\text-}\)type semiconductor is the same as the hole concentration in a \(\mathrm{p\text{-}}\)type semiconductor. An external field (electric) is applied across each of them. Compare the currents in them.
1.
current in \(\mathrm{n\text-}\)type \(>\) current in \(\mathrm{p\text{-}}\)type.
2.
no current will flow in \(\mathrm{p\text{-}}\)type, current will only flow in \(\mathrm{n\text-}\)type.
3.
current in \(\mathrm{n\text-}\)type \(=\) current in \(\mathrm{p\text{-}}\)type.
4.
current in \(\mathrm{p\text{-}}\)type \(>\) current in \(\mathrm{n\text-}\)type.
| Statement A: | A Zener diode is connected in reverse bias when used as a voltage regulator. |
| Statement B: | The potential barrier of \(\mathrm{p\text-n}\) junction lies between \(0.2\) V to \(0.3\) V. |
| 1. | Statement A is correct and Statement B is incorrect. |
| 2. | Statement A is incorrect and Statement B is correct. |
| 3. | Statement A and Statement B both are correct. |
| 4. | Statement A and Statement B both are incorrect. |
For the given circuit, the input digital signals are applied at the terminals \(A\), \(B\) and \(C\). What would be the output at terminal \(Y\)?
| 1. |  |
| 2. |  |
| 3. |  |
| 4. |  |
Following diagram performs the logic function of:
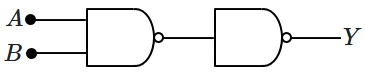
1. AND gate
2. NAND gate
3. OR gate
4. XOR gate
The barrier potential of a \(\mathrm{p\text-n}\) junction diode does not depend on:
| 1. | diode design | 2. | temperature |
| 3. | forward bias | 4. | doping density |
If a full-wave rectifier circuit is operating from \(50~\text{Hz}\) mains, the fundamental frequency in the ripple will be:
1. \(25~\text{Hz}\)
2. \(50~\text{Hz}\)
3. \(70.7~\text{Hz}\)
4. \(100~\text{Hz}\)
Reverse bias applied to a junction diode:
| 1. | lowers the potential barrier |
| 2. | raises the potential barrier |
| 3. | increases the majority carrier current |
| 4. | increases the minority carrier's current |
The current \((I)\) in the circuit will be:
| 1. | \(\dfrac{5}{40}~\text{A}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{5}{50}~\text{A}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{5}{10}~\text{A} \) | 4. | \(\dfrac{5}{20}~\text{A}\) |
The following truth table represent which logic gate:
| A | B | C |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
1. XOR
2. NOT
3. NAND
4. AND
For the given circuit of the \(\mathrm{p\text-n}\) junction diode, which of the following statements is correct?

| 1. | In F.B. the voltage across \(R\) is \(V.\) |
| 2. | In R.B. the voltage across \(R\) is \(V.\) |
| 3. | In F.B. the voltage across \(R\) is \(2V.\) |
| 4. | In R.B. the voltage across \(R\) is \(2V.\) |









