Select Chapter Topics:
In an oscillating spring mass system, a spring is connected to a box filled with the sand. As the box oscillates, sand leaks slowly out of the box vertically so that the average frequency \(\omega~(t)\) and average amplitude \(A~(t)\) of the system changes with time \(t.\) Which of the following options systemically depicts these changes correctly?
| 1. | 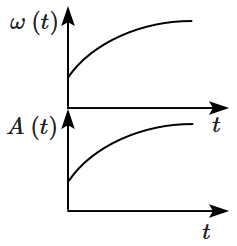 |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Subtopic: Spring mass system |
Level 3: 35%-60%
NEET - 2025
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
Two identical point masses \(P\) and \(Q,\) suspended from two separate massless springs of spring constant \(k_1\) and \(k_2,\) respectively, oscillate vertically. If their maximum speeds are the same, the ratio \(\left(\dfrac{A_Q}{A_P} \right)\) of the amplitude \(A_Q\) of mass \(Q \) to the amplitude \(A_P\) of mass \(P\) is:
| 1. | \(\sqrt{\dfrac{k_2}{k_1}}\) | 2. | \(\sqrt{\dfrac{k_1}{k_2}}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{k_2}{k_1}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{k_1}{k_2}\) |
Subtopic: Spring mass system |
54%
Level 3: 35%-60%
NEET - 2025
Please attempt this question first.
Hints
Please attempt this question first.
If \(x = 5 \mathrm {sin }\left(\pi t+ {\dfrac {\pi} 3}\right)~\text m\) represents the motion of a particle executing simple harmonic motion, the amplitude and time period of motion, respectively are:
| 1. | \(5~\text m, 2~\text s\) | 2. | \(5~\text {cm}, 1~\text s\) |
| 3. | \(5~\text m, 1~\text s\) | 4. | \(5~\text {cm}, 2~\text s\) |
Subtopic: Simple Harmonic Motion |
74%
Level 2: 60%+
NEET - 2024
Hints
If the mass of a bob in a simple pendulum is increased to thrice its original mass and its length is made half its original length, then the new time period of oscillation is \( \dfrac{x}{2}\) times its original time period. The value of \(x\) is:
| 1. | \(\sqrt2\) | 2. | \(2\sqrt3\) |
| 3. | \(4\) | 4. | \(\sqrt3\) |
Subtopic: Angular SHM |
68%
Level 2: 60%+
NEET - 2024
Hints
If \(T_1,T_2,T_3,T_4\) and \(T_5\) represent the tension in the string of a simple pendulum when the bob is at the left extreme, right extreme, mean, any intermediate left and any intermediate right positions, respectively. Then, which of the following relations are correct?
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
| (A) | \(T_1=T_2\) | (B) | \(T_3>T_2\) |
| (C) | \(T_4>T_3\) | (D) | \(T_3=T_4\) |
| (E) | \(T_5>T_2\) | ||
| 1. | (A), (B) and (C) only | 2. | (B), (C) and (D) only |
| 3. | (A), (B) and (E) only | 4. | (C), (D) and (E) only |
Subtopic: Angular SHM |
68%
Level 2: 60%+
NEET - 2024
Hints
A particle executing simple harmonic motion with amplitude \(A\) has the same potential and kinetic energies at the displacement:
| 1. | \(2\sqrt{A}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{A}{2}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{\mathrm{A}}{\sqrt{2}}\) | 4. | \(A\sqrt{2}\) |
Subtopic: Energy of SHM |
80%
Level 1: 80%+
NEET - 2024
Hints
The two-dimensional motion of a particle, described by \(\vec{r}=(\hat{i}+2\hat{j}) A~\text{cos}(\omega t) \) is a/an:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| (A) | parabolic path |
| (B) | elliptical path |
| (C) | periodic motion |
| (D) | simple harmonic motion |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| 1. | (B), (C), and (D) only |
| 2. | (A), (B), and (C) only |
| 3. | (A), (C), and (D) only |
| 4. | (C) and (D) only |
Subtopic: Types of Motion |
53%
Level 3: 35%-60%
NEET - 2024
Hints
The displacement-time \((x\text-t)\) graph of a particle performing simple harmonic motion is shown in the figure. The acceleration of the particle at \(t=2\) s is:


| 1. | \(-\dfrac{\pi^2}{16} ~\text{ms}^{-2}\) | 2. | \(\dfrac{\pi^2}{8}~ \text{ms}^{-2}\) |
| 3. | \(-\dfrac{\pi^2}{8} ~\text{ms}^{-2}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{\pi^2}{16} ~\text{ms}^{-2}\) |
Subtopic: Simple Harmonic Motion |
67%
Level 2: 60%+
NEET - 2023
Hints
A simple pendulum oscillating in air has a period of \(\sqrt3\) s. If it is completely immersed in non-viscous liquid, having density \(\left(\dfrac14\right)^{\text{th}}\) of the material of the bob, the new period will be:
| 1. | \(2\sqrt3\) s | 2. | \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt3}\) s |
| 3. | \(2\) s | 4. | \(\dfrac{\sqrt 3}{2}\) s |
Subtopic: Angular SHM |
54%
Level 3: 35%-60%
NEET - 2023
Hints
Two pendulums of length \(121~\text{cm}\) and \(100~\text{cm}\) start vibrating in phase. At some instant, the two are at their mean position in the same phase. The minimum number of vibrations of the shorter pendulum after which the two are again in phase at the mean position is:
| 1. | \(8\) | 2. | \(11\) |
| 3. | \(9\) | 4. | \(10\) |
Subtopic: Angular SHM |
71%
Level 2: 60%+
NEET - 2022
Hints






