4.22 The rate constant for the decomposition of N2O5 at various temperatures is given below:
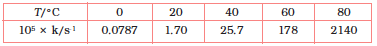
Draw a graph between ln k and 1/T and calculate the values of A and Ea. Predict the rate constant at 30° and 50°C.

© 2026 GoodEd Technologies Pvt. Ltd.